Lesson 9: Networking¶
Who is this talk for?¶
Someone with little or no networking knowledge.
ECE/CS 372 at OSU covers this content, more or less
What is a network?¶
“a group or system of interconnected people or things“
To us, a network is:
- Electronic devices
- Sending signals over wire, fiber, or radio
- Communicating data using a standardized protocol
What is a protocol?¶
“A set of agreed upon rules for communication“
- Defines sequence & format of packets being sent
The OSI Model¶
Open Systems Interconnection
- Layers of abstraction
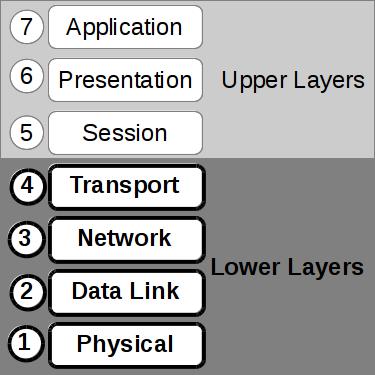
Note
“Create a layer of easily localized functions so that the layer could be totally redesigned and its protocols changed in a major way... without changing the services expected from and provided to adjacent layers”
Layer 1: Physical¶
Networking Hardware
- Connector shapes
- Wire, optical fiber, or radio signal specifications

RS-232
Layer 2: Data Link¶
MAC: Media Access Control
- MAC address should be globally unique
- ARP: Address Resolution Protocol (between layer 2 & 3)
- NDP (neighbor discovery protocol) used in IPv6
- Flow control & error checking
Layer 4: Transport¶
Interact directly with program same-order delivery, reliability, flow control, and congestion avoidance
| TCP: | Transmission Control Protocol |
|---|
- used by HTTP, HTTPS, SMTP, POP3, IMAP, SSH, FTP, Telnet
| UDP: | User Datagram Protocol |
|---|
- No error checking built in
- No retransmission delays
- VoIP, media, games
Get your hands dirty¶
In a linux terminal run::
ip a
These will display information about your network interfaces.
See also:
ifconfig
iwconfig
Example output:¶
user@host:~$ ip a
...
2: eth2: <NO-CARRIER,BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state DOWN qlen 1000
link/ether 33:77:00:44:66:33 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
3: wlan1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP qlen 1000
link/ether 24:77:33:44:55:66 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.1.55/24 brd 192.168.1.255 scope global wlan1
inet6 fe80::2677:3ff:fed4:538c/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
Netmask:¶
| Decimal IP Address | Binary IP Address |
| 192.168.1.55 | 11000000.10101000.00000001.00110111 |
| 255.255.255.0 | 11111111.11111111.11111111.00000000 |
| Part of address | Corresponding address |
| Network (Decimal) | 192.168.1.0 |
| Network (Binary) | 11000000.10101000.00000001.00000000 |
| Host (Decimal) | 0.0.0.55 |
| Host (Binary) | 00000000.00000000.00000000.00110111 |
Available Hosts: 192.168.1.[1-254]
Broadcast address: 192.168.1.255
Netmask Example:¶
| Decimal IP Address | Binary IP Address |
| 192.168.90.55 | |
| 255.255.192.0 |
Netmask Example:¶
| Decimal IP Address | Binary IP Address |
| 192.168.90.55 | 11000000.10101000.01011010.00110111 |
| 255.255.192.0 | 11111111.11111111.11000000.00000000 |
| Part of address | Corresponding address |
| Network (Decimal) | 192.168.64.0 |
| Network (Binary) | |
| Host (Decimal) | 0.0.26.55 |
| Host (Binary) |
Netmask Example:¶
| Decimal IP Address | Binary IP Address |
| 192.168.90.55 | 11000000.10101000.01011010.00110111 |
| 255.255.192.0 | 11111111.11111111.11000000.00000000 |
| Part of address | Corresponding address |
| Network (Decimal) | 192.168.64.0 |
| Network (Binary) | 11000000.10101000.01000000.00000000 |
| Host (Decimal) | 0.0.26.55 |
| Host (Binary) | 00000000.00000000.00011010.00110111 |
Available Hosts: 192.168.[64-127].[1-254]
Broadcast Address: 192.168.127.255
Routes¶
user@host:~$ route
Kernal IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
default foo.osuosl 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 wlan1
link-local * 255.255.0.0 U 1000 0 0 wlan1
192.168.1.0 * 255.255.255.0 U 2 0 0 wlan1
user@host:~$ route -n
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
0.0.0.0 192.168.1.1 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 wlan1
169.254.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 U 1000 0 0 wlan1
192.168.1.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 2 0 0 wlan1
Bootstrapping¶
What happens when your computer connects to a network?
- Duplex and speed negotiation
- Static or dynamic configuration is applied
Static Configuration¶
Must in advance know:
- IP Address
- Netmask
- Default Gateway
- DNS Servers (optional in some cases)
Dynamic Configuration¶
All of the statically defined parameters are retrieved over the network via DHCP
But how do you communicate over the network without a network configuration?
Public vs Private Address¶
| NAT: | Network Address Translation |
|---|
- lose end-to-end traceability
- hides internal network topology
- allows use of private IP’s over public internet
- conserves limited public IP’s
Control Layer¶
Connection oriented vs Connectionless
Collisions¶
- CSMA CA
- All Wireless networks use this Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collisions Avoidance
- CSMA CD
- Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collisions Detection
Why is this important?