Lesson 16: Email¶
- Email service
- How it works
- Configuration Postfix
- Planning
Email: System Components¶
- Mail User Agent (MUA)
- Mail Transport Agent (MTA)
- Delivery Agent (MDA)
- Access Agent (MAA)
Note
| MUA: |
|
|---|---|
| MTA: |
|
| MDA: |
|
| MAA: | access to mail store (i.e IMAP, POP) |
Email: System Components¶
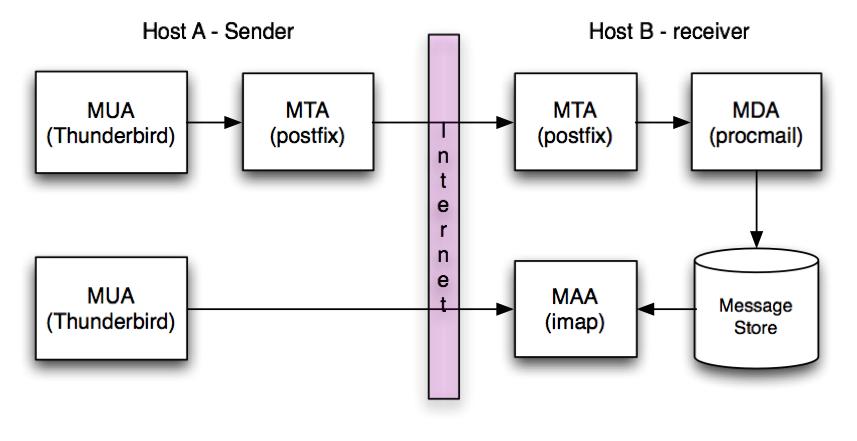
Note
The most confusing part about email is understanding the routing. Knowing the different components is important to fully grasping it.
Transport Agents¶
Accept mail form user agent
| Postfix: | More common, easier to configure & use |
|---|---|
| Sendmail: | Highly configurable, steep learning curve |
| Exim: | Similar to Postfix |
| Qmail: | Logging is horrid, but some people like it |
Note
Postfix is the easiest to learn and understand, but queue management is a “black box”
Sendmail & qmail is great for high volume sites, but postfix/exim still perform great.
Sendmail has great options for queue management
- Features to look out for:
- SASL (authenticated SMTP)
- Queue Management
Delivery Agents & Message Stores¶
procmail – great filtering
maildrop – newer procmail-like
mail.local
- Message Stores
- mbox – one large file, locking problems
- maildir – one file per message, great for IMAP
Note
Consider scaling issues for the mailstore.
Generally maildir is the best & most compatible option
Anatomy of a Mail Message¶
- Envelope
- Destination email address
- Headers
- Record of variety of important information
- Great for tracking down problems
Body of the message
Note
- Headers:
- Know how to identify and track queue id’s
- Originator starts at the bottom
- Headers can be forged
- X- Headers non-RFC headers
- Message ID is always unique
MTA Log Files¶
- Track emails via queue ID
- Look something like: 03CE18819A
Tracking via message ID
- Informational fields
- to, from, status, relay, etc
Log files differ between each MTA
Note
Being able to read log files is important.
Configuring Postfix¶
- /etc/postfix
- main.cf – main config file
- master.cf – postfix process config file
- /etc/aliases – local email forwarding
- Set to relay email to central MTA
- relayhost = [smtp.osuosl.org]
- myorigin = osuosl.org
- /etc/aliases – root: foo@gmail.com
Note
- relayhost: [smtp.osuosl.org] vs. osuosl.org
- [smtp.osuosl.org] goes directly to smtp.osuosl.org
- ‘osuosl.org’ does DNS lookup and uses MX
Make sure you run “newaliases” after updating /etc/aliases
Reloading postfix is ideal too
- To test email:
- echo “this is a test” | mail root@localhost
Sendmail¶
- Config files created via m4
- Makefile
Always edit the .mc files not the .cf files
Remember to rebuild .cf files with make
Extremely configurable
Note
Config files in /etc/mail usually Primary file to edit should be sendmail.mc
Email: Viruses & Spam¶
- Virus
- Clamav
- Ensure freshclam is running too
- Spam
- Spamassassin
- All-in-one
- Amavis
Check abuse emails
Note
Make sure you have enough CPU & RAM for Spam checking Neglecting abuse emails may get you blacklisted For larger infrastructures, have dedicated machines to process spam Important to keep these updated
Email: Infrastructure Implementation¶
- Small sites
- Can have MTA/MDA/etc all on the same server
- Medium sites
- Separate MTA from MDA
- Large sites
- Split outgoing mail and incoming
Note
Consider resources, redundancy, & scalability. MDA is hardest to scale.
- Look at Cyrus Murder for large scalability
- dovecot is another option
Email: Security¶
- On General servers:
- Only listen on localhost
- Don’t allow other hosts to relay through it
- Relay all outbound mail through central host
- On Email servers:
- Restrict relaying to trusted networks
- Implement antivirus & spam protection
Note
Always test new configurations to ensure spammers can’t relay mail through your server Having dedicate outbound servers will ensure they always catch spam/viruses/etc